ETFs Simplified: Your Guide to Smart Investing — Part II.
Unlocking the Power of Exchange-Traded Funds for Every Investor
In a previous article within this series, I introduced the basic concepts of ETFs. This article covers strategies and types of ETFs on a very high level, and above all, the most useful you will find is the link to download. CSV file having all the ETFs traded in the US with their return and dividends since they started trading. Historical Returns and Dividends are processed up to September 30, 2024. Explore a wealth of free information you won’t find anywhere else online. Our resources provide valuable insights and data at no cost, making accessing essential knowledge easier.
Types of ETFs and Their Investment Strategies
The world of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) is extensive, offering a wide range of options tailored for various investment strategies and asset classes. From index ETFs that track major market indexes to sector and industry ETFs focusing on specific areas, investors have numerous choices available. This diverse selection can be both exciting and overwhelming for those looking to invest in ETFs
Index ETFs
Index ETFs aim to match the performance of a specific market index, like the S&P 500 or the Nasdaq Composite. They are a simple and affordable way to invest in a broad market or sector. By tracking the index, these ETFs offer a diversified investment that mirrors the market’s performance. For example, the table below has a list of ETFs tracking the eleven S&P 500 sectors.
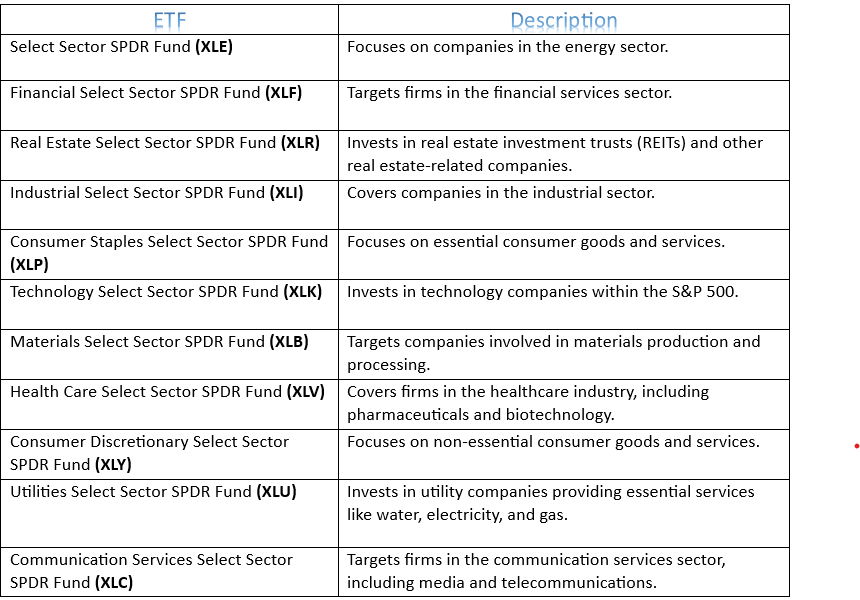 ETF’s tracking S&P 500 Index Sectors
ETF’s tracking S&P 500 Index SectorsHow to Choose the Right ETF for Your Portfolio
Choosing the right exchange-traded funds (ETFs) is key to reaching your financial goals. It doesn’t matter if you’re new or experienced. The main thing is to think about your investment goals, risk tolerance, and portfolio diversification needs.
As Warren Buffett once said, “Risk comes from not knowing what you’re doing.”When looking at ETFs, focus on their expense ratios and trading volume. Low expense ratios can boost your returns. High trading volume means you can easily buy and sell shares.
- Choose ETFs that closely match their underlying index or benchmark. This helps you get the investment exposure you want.
- Spread your ETFs across different sectors, asset classes, and investment strategies. This reduces risk and improves your portfolio’s performance.
- Think about your risk tolerance when picking ETFs. Pick funds that fit your comfort level with market ups and downs. For example, I use SPHD ETF, which exhibits both high dividend yields and low volatility to play put and covered call options.
Expense Ratios
The main fee is the expense ratio. It’s the yearly cost of managing and running the fund. Expense ratios differ a lot, from very low fees to higher ones. It’s key to compare these fees to choose wisely.
Trading Costs
There are also trading costs like bid-ask spreads and commissions. The bid-ask spread affects the buying and selling prices. Commissions from brokers can also cut into your returns. Knowing these costs helps in making a better investment choice.
Tax Implications of ETF Investing
Investors in exchange-traded funds (ETFs) need to watch out for taxes. ETFs are often more tax-friendly than mutual funds. But, they can still cause taxes that investors should know about.
Capital gains are a big deal. ETFs, like stocks, can make money when they sell securities for more than they bought them for. This profit is passed on to the investors, who have to report it on their taxes. Choosing ETFs with low turnover can help reduce these gains.
Another thing to think about is dividend distributions. Many ETFs hold stocks that pay dividends. These dividends are taxed, so investors need to be ready for the tax bill.
Download Historical and current dividend and return information for all the ETFs traded in the US.” 📈
- Understand the tax-efficiency of the ETF: Look for ETFs with low portfolio turnover and tax-efficient index tracking strategies to minimize capital gains distributions.
- Utilize tax-loss harvesting: This strategy involves selling underperforming ETFs to offset capital gains, reducing your overall tax liability.
- Consider holding ETFs in tax-advantaged accounts: Holding ETFs in retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s or IRAs, can help defer or eliminate taxes on dividends and capital gains.
Building a Diversified ETF Portfolio
Creating a diversified ETF portfolio is key to managing risk and reaching your investment goals. By spreading your investments across different areas, you can balance your portfolio. This matches your risk level and time frame.
Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation means dividing your investments into different types, like stocks, bonds, and real estate. A good strategy can balance your portfolio’s risk and return. Think about your goals, how much risk you can take, and your time frame when picking your mix.
- Diversify by mixing domestic and international ETFs.
- Add fixed-income ETFs for stability and to balance your stock risk.
- Look into sector-specific ETFs to focus on industries or themes that fit your investment goals.
Rebalancing Your Portfolio
Regular rebalancing keeps your portfolio aligned with your goals. As markets change, your portfolio’s mix will too. Rebalancing means adjusting your investments to match your target mix.
- Check your portfolio’s mix at least once a year to see if it’s off track.
- Adjust your investments to get back to your desired portfolio diversification and risk management levels.
- Think about taxes when rebalancing to keep your goal-based investing strategy strong.
By sticking to a solid asset allocation and rebalancing plan, you can build a diverse ETF portfolio. This helps you handle market ups and downs and reach your long-term financial goals.
ETF Trading Strategies and Best Practices
Investors have many ETF trading strategies to choose from. Knowing these trading strategies and following best practices can improve how we manage our investments.
One popular method is using market orders. This lets you buy or sell an ETF at the current price. It’s simple but doesn’t let you control the price. Limit orders, however, let you set a price you’re willing to buy or sell at. This gives you more control over when you enter or exit the market.
Stop-loss orders are another useful tool. They automatically sell an ETF if it hits a certain price. This helps protect your investments by limiting losses. Dollar-cost averaging is also effective. It involves investing a fixed amount regularly to grow your ETF portfolio.
You can better navigate the markets by learning and using these ETF trading strategies and best practices. This helps you make smarter investment choices.
Also, some ETFs use leverage or derivatives, which can increase both gains and losses. Investors should also watch out for counterparty risk in ETFs that use swap agreements or complex structures.
Download Historical and current dividend and return information for all the ETFs traded in the US." 📈
Show Your Support! If you enjoyed this article, give a round of applause 👏 and leave a comment. Your feedback motivates us to create more quality content.
- **Subscribe for Free! Join my email list to receive monthly updates on new and inactive ETFs, stocks, and mutual funds, including detailed monthly returns, and for more insights and discussions about investments and financial markets.
- Connect with Me! Follow me on LinkedIn.
ETFs Simplified: Your Guide to Smart Investing — Part II. was originally published in The Capital on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.

 3 months ago
58
3 months ago
58









 English (US) ·
English (US) ·