Infinite Money Glitch: Michael Saylor’s Convex Payoff Model — Turning Bitcoin Volatility into Strategic Advantage
Michael Saylor’s strategic use of Bitcoin as a corporate treasury asset is a masterstroke in exploiting market volatility through a convex payoff model. It’s not just financial engineering; it’s an intricate game-theoretic approach that transforms Bitcoin’s inherent unpredictability into a tool for long-term wealth creation. Let’s delve into this innovative strategy, dissecting its mechanics, its implications, and the mathematical principles underpinning it, while weaving in examples with game-theory dynamics.

What is a Convex Payoff? A Simplified Explanation
To grasp the genius of Saylor’s strategy, let’s unpack the idea of convexity. A convex payoff refers to a scenario where gains increase exponentially with favorable outcomes, while losses are linear or capped. In finance, it’s akin to holding options: when prices rise, the upside is magnified, but when they fall, the downside is contained.
Think of it This Way:
Imagine you’re holding a lottery ticket that costs $10. If you lose, you’re out $10. But if you win, your payoff could be $1 million. This asymmetry — small downside, massive upside — is what defines convexity.
Michael Saylor has effectively turned MicroStrategy into the corporate equivalent of holding a massive Bitcoin option. His strategy leverages Bitcoin’s price volatility to amplify returns during bull runs while managing risks during downturns.
The Mechanics of Saylor’s Convexity
Saylor’s convex payoff model is built on a foundation of strategic tools: debt financing, equity programs, yield generation, and market timing. Here’s how each component works:
1. Convertible Debt: A Built-In Hedge
MicroStrategy funds Bitcoin purchases through convertible bonds, which allow bondholders to convert debt into equity if the company’s stock appreciates.
- Why This Matters:
- If Bitcoin prices soar, MicroStrategy’s stock rises, enabling bondholders to convert debt to equity, which aligns incentives.
- If Bitcoin prices fall, MicroStrategy only pays fixed interest on the bonds, minimizing downside risks.
- Convexity in Action:
- Gains from Bitcoin appreciation amplify equity value, while fixed interest costs contain losses.
2. At-The-Market (ATM) Equity Offerings
MicroStrategy issues shares at prevailing market prices to raise capital for additional Bitcoin purchases.
- Why This Matters:
- During bull markets, ATM offerings capitalize on elevated stock prices to secure premium funding.
- Proceeds are reinvested into Bitcoin, amplifying holdings and creating a positive feedback loop.
- Convexity in Action:
- Increased Bitcoin acquisitions during bull runs outpace the dilutive effect of issuing new shares.
3. Yield Generation Strategies
MicroStrategy is exploring ways to generate yield from its Bitcoin holdings, including lending and staking opportunities.
- Why This Matters:
- These strategies create a steady cash flow, offsetting the need for additional equity or debt during bearish cycles.
- Convexity in Action:
- Yield diversifies income streams, reducing reliance on Bitcoin price appreciation while preserving upside potential.
4. Strategic Use of Volatility
Rather than fearing Bitcoin’s price swings, Saylor treats volatility as an asset. Corrections are buying opportunities, and bull runs are moments to optimize equity programs.
- Convexity in Action:
- Buying Bitcoin during price dips reduces cost basis, while unrealized gains during rallies enhance balance sheet strength.
The Game Theory of MicroStrategy’s Bitcoin Strategy
MicroStrategy’s approach can be modeled as a dynamic game where players — investors, regulators, and competitors — interact under conditions of uncertainty. Each move impacts the equilibrium, creating opportunities and risks.
Key Players and Strategies
MicroStrategy (MSTR):
- Objective: Maximize Bitcoin holdings and long-term shareholder value.
- Strategies: Issue debt, acquire Bitcoin, and leverage volatility.
Investors:
- Objective: Optimize risk-adjusted returns.
- Strategies: Buy, hold, or sell based on Bitcoin price trends and MicroStrategy’s execution.
Regulators:
- Objective: Ensure compliance and systemic stability.
- Strategies: Introduce rules to balance innovation and risk.
Mathematical Representation of the Payoff
Let’s quantify the payoff using a simplified model:
Variables:
- H: Bitcoin holdings (446,400 BTC).
- P: Bitcoin price.
- S: MicroStrategy stock price.
- L: Leverage multiplier (from debt and equity).
- C: Fixed costs (e.g., interest, operational expenses).
Payoff Function:
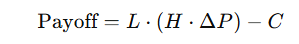
Convexity Explained:

Scenarios to Illustrate Convexity
Scenario 1: Bitcoin Drops to $80K
- Impact:
- Short-term unrealized losses appear on financial statements.
- Stock price declines due to market sentiment.
- Saylor’s Move:
- Use ATM offerings to acquire more Bitcoin at discounted prices.
- Prepare for a future recovery, reducing the cost basis.
Scenario 2: Bitcoin Stabilizes at $200K
- Impact:
- Stability attracts institutional investors.
- Unrealized gains improve reported earnings under FASB rules.
- Saylor’s Move:
- Generate yield through lending programs.
- Execute stock splits to broaden investor base.
Scenario 3: Bitcoin Surges to $400K
- Impact:
- Unrealized gains skyrocket, boosting earnings and stock price.
- Increased market capitalization attracts retail and institutional investors.
- Saylor’s Move:
- Leverage elevated stock prices for ATM offerings to secure liquidity for future acquisitions.
Strategic Implications
1. Investor Dynamics
Investors must navigate a game of asymmetric information, balancing potential Bitcoin gains against dilution risks. Understanding convexity is crucial for making informed decisions.
2. Regulatory Oversight
Regulators act as a stabilizing force, ensuring transparency and compliance. The FASB’s fair value rules reduce informational asymmetry, aligning player incentives.
3. Institutional Adoption
As institutions embrace Bitcoin, MicroStrategy’s strategy could shift the Nash equilibrium of corporate treasury management, normalizing Bitcoin as a reserve asset.
Critiques and Risks
Saylor’s strategy, while innovative, is not without challenges:
- Leverage Risks: Excessive debt could strain financial flexibility during prolonged bear markets.
- Earnings Volatility: The fair value model amplifies quarterly earnings swings, testing investor patience.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Aggressive financial engineering may invite heightened scrutiny.
Final Thoughts: Mastering the Infinite Money Glitch
Michael Saylor’s convex payoff model is a masterclass in turning volatility into strategic advantage. By leveraging financial tools, yield strategies, and market timing, MicroStrategy has created a playbook that maximizes asymmetric returns.
Whether Bitcoin stabilizes, crashes, or skyrockets, Saylor’s approach positions MicroStrategy to thrive in any scenario. It’s not just about Bitcoin — it’s a revolutionary way to think about corporate finance in a volatile world.
Infinite Money Glitch: Michael Saylor’s Convex Payoff Model — Turning Bitcoin Volatility into… was originally published in The Capital on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.

 2 days ago
161
2 days ago
161







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·