Swimming with Sharks: Navigating Exotic Option Trading for MSTR — Beware the Monsters Below
With price movements closely tied to Bitcoin’s dramatic swings, MSTR is the perfect playground for applying sophisticated hedging and exotic option strategies. For traders seeking to understand and master exotic options, MSTR offers real-world challenges and opportunities to test theories, refine tactics, and capture profits.
This guide provides a roadmap for transitioning from vanilla options to advanced exotic instruments like multi-asset and path-dependent options, highlighting strategies tailored for MSTR’s dynamic price behavior.

Step 1: Start with Vanilla Options — The Basics
Vanilla options — puts and calls — are the gateway to understanding advanced trading techniques. MSTR’s volatility, often exceeding 80%, makes it an excellent candidate for vanilla options, offering high potential for both profit and risk mitigation.
Why Vanilla Options Matter
- High Implied Volatility (IV): MSTR’s frequent price swings make strategies like straddles and strangles lucrative.
- Dynamic Hedging Practice: Frequent price adjustments allow traders to practice managing delta-neutral positions.
Strategy: ATM Straddles
An at-the-money (ATM) straddle involves buying a call and a put at the same strike price. The goal is to profit from significant price movement in either direction.
Example:
- Stock Price: $370
- Call Premium: $25
- Put Premium: $20
- Total Cost: $45 per share
Breakeven Points:
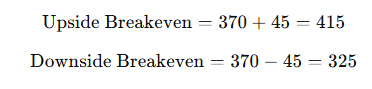
Profit Scenarios:
MSTR rises to $450:
- Call Value: $450 — $370 = $80
- Total Profit: $80 — $45 = $35 per share.
MSTR falls to $320:
- Put Value: $370 — $320 = $50
- Total Profit: $50 — $45 = $5 per share.
The straddle works best when MSTR moves sharply, regardless of direction.
Step 2: Introducing Barrier and Binary Options
Barrier and binary options are excellent tools for leveraging MSTR’s volatility. These instruments activate or deactivate based on specific price thresholds.
Understanding the Concepts
- Barrier Options: Activate (knock-in) or deactivate (knock-out) once the stock hits predefined levels.
- Binary Options: Offer fixed payouts depending on whether the stock breaches a target price.
Strategy: Knock-In Barrier Options
Barrier options allow traders to speculate or hedge without upfront exposure unless a specific price is breached.
Example:
- Knock-In Call Strike Price: $400
- Activation Level: $390
- Premium: $15 per share
Profit Scenarios:
MSTR hits $450:
- Call activates at $390.
- Intrinsic Value: $450 — $400 = $50
- Net Profit: $50 — $15 = $35 per share.
MSTR never hits $390:
- Option expires worthless, resulting in a $15 loss per share.
Step 3: Multi-Asset Options and Correlation Hedging
MSTR’s correlation with Bitcoin enables multi-asset strategies that leverage this relationship for enhanced profitability.
Key Metrics
- Volatility Matrix: A combined volatility matrix for MSTR and Bitcoin helps optimize hedging strategies.
- Cross-Gammas: These quantify how changes in Bitcoin affect MSTR options.
Strategy: Basket Options
Understanding Basket Options:
A basket option derives its payoff from the average performance of multiple underlying assets — in this case, MSTR stock and Bitcoin. This approach allows traders to hedge or speculate on the combined movements of both assets.
Example:
Asset Details:
- MSTR Current Price: $450
- Bitcoin Current Price: $98,000
- Basket Weights: Equal weights for simplicity (50% each).
Basket Strike Price Calculation:
- Average Price of Assets:
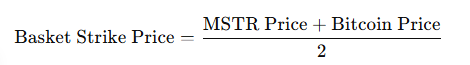
- Substituting values:
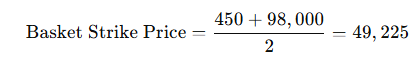
- Premium: Assume a premium of $500 per share.
Profit Scenarios:
Scenario 1:
- MSTR rises to $500, Bitcoin to $100,000.
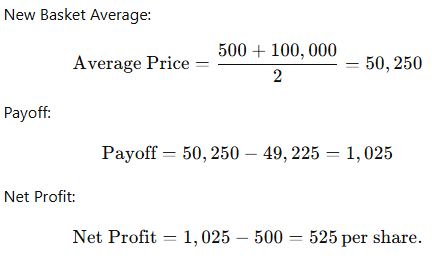
Scenario 2:
- MSTR drops to $420, Bitcoin to $95,000.
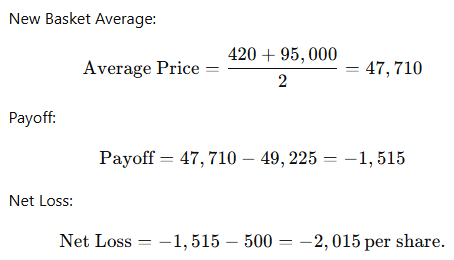
Key Considerations:
- Volatility Matrix: Understanding the covariance between MSTR and Bitcoin is crucial for effective hedging.
- Cross-Gammas: Quantifying how changes in Bitcoin’s price affect MSTR options helps in managing risk.
By employing basket options, traders can capitalize on the intertwined movements of MSTR and Bitcoin, potentially enhancing profitability through strategic hedging and speculation.
Step 4: Path-Dependent Options for Volatility Exploitation
Path-dependent options consider the sequence of price changes, not just the final price.
Strategies for Path Dependence
- Lookback Options: These allow traders to buy at the lowest price or sell at the highest price during the option’s life.
- Asian Options: Averaging the stock price over time smooths out short-term volatility.
Example: Lookback Call
- Strike Price: $370
- Lowest Price: $320
- Premium: $50 per share
Profit Scenarios:
MSTR peaks at $450:
- Payoff: $450 — $320 = $130
- Net Profit: $130 — $50 = $80 per share.
MSTR peaks at $390:
- Payoff: $390 — $320 = $70
- Net Profit: $70 — $50 = $20 per share.
Step 5: Implementing Higher-Order Exotic Options with Detailed Calculations
Higher-order exotic options offer traders dynamic flexibility, combining structured payoff scenarios with adaptability to volatile market conditions. For a stock like MicroStrategy (MSTR), with its notorious price swings driven by Bitcoin’s volatility, these options provide a robust mechanism to lock in profits while maintaining exposure to potential upside.
Strategy: Shout Options
Shout options allow traders to lock in profits at a chosen point during the life of the option while retaining the possibility of further gains. They are particularly valuable in high-volatility scenarios like MSTR’s.
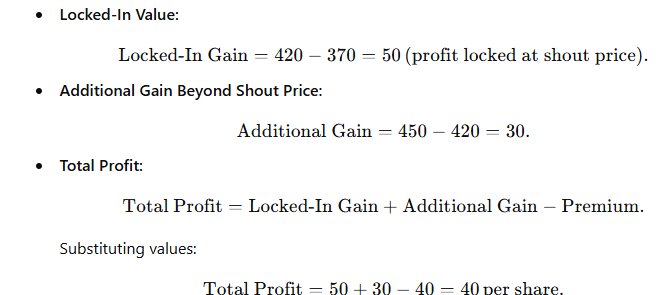
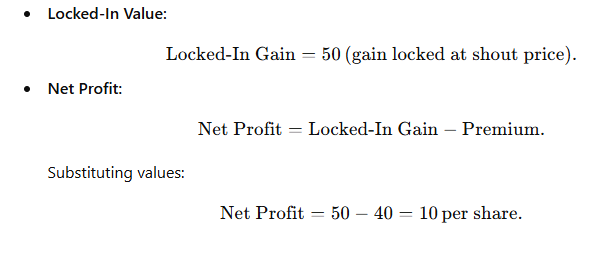
Example Setup:
- Strike Price: $370
- Initial Shout Price: $420
- Premium: $40 per share
- Expiration: 1 month
Profit Calculations:
Scenario 1: MSTR rises to $450
Scenario 2: MSTR drops to $360
Step 6: Addressing Non-Time-Homogeneous Risks
MSTR’s volatility often spikes around Bitcoin-related events, such as ETF approvals or market announcements. These sudden, event-driven fluctuations require hedging strategies that account for differences in implied volatility (IV) over time.
Strategies: Calendar Spreads
Calendar spreads take advantage of differences in IV between short-term and long-term options. By selling short-term options and buying longer-term ones at the same strike, traders can profit from IV decay.
Example Setup:
- Short-Term Call Strike: $370, Premium: $20
- Long-Term Call Strike: $370, Premium: $30
Profit Calculation:
- Short-Term IV drops:
- Value of Short-Term Call: $10 (IV decay reduces its value).
- Value of Long-Term Call: $35 (less affected by IV decay due to longer duration).
- Net Profit:

Strategies: Forward Volatility Trading
Forward-start options prepare for anticipated volatility spikes, allowing traders to lock in favorable IV rates before the market reacts to significant events.
Example Setup:
- Anticipated Event: Bitcoin ETF approval
- Current IV: 70%
- Expected IV Spike: 90%
- Forward-Start Option Premium: Calculated using Black-Scholes.
Risk Management Techniques for Exotic Options
Managing exotic options requires a robust framework to mitigate transaction costs, account for volatility skew, and prevent catastrophic losses.
1. Transaction Costs
Frequent rebalancing, especially for path-dependent options, can erode profits. Optimize frequency by balancing hedging precision with transaction costs.
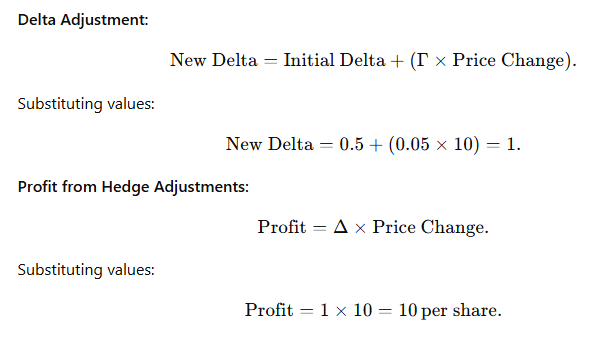
Example: Gamma Scalping
- Initial Delta: 0.5
- Gamma: 0.05
- Price Increase: $10
2. Volatility Skew
MSTR’s out-of-the-money (OTM) calls often have higher IV due to Bitcoin’s upside potential. Adjust pricing models to reflect this skew and recalibrate hedging positions dynamically.
3. Stop-Loss Levels
Set realistic thresholds to avoid catastrophic losses during extreme volatility. For example, a stop-loss at a 20% decline in MSTR’s price can help preserve capital without prematurely exiting profitable trades.
Through tools like shout options, calendar spreads, and gamma scalping, traders can harness volatility, anticipate IV changes, and dynamically hedge positions. A mathematically rigorous approach ensures precision, transforming MSTR’s turbulence into calculated profitability.
Swimming with Sharks: Navigating Exotic Option Trading for MSTR — Beware the Monsters Below was originally published in The Capital on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.

 1 month ago
44
1 month ago
44







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·